This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Bluetooth Mesh: Technology Overview, Examples, Alternatives, and First-Hand Experience


Andrey Solovev
Chief Technology Officer, PhD in Physics and Mathematics

Anna Petrova
Writer With Expertise in Covering Electronics Design Topics
Learn from our experiences about Bluetooth mesh networking, how and where to use it. We’ll tell you about the design and operation principles of this protocol and compare it with similar technologies, such as Zigbee and Thread. In our Bluetooth mesh guide, you’ll learn about the advantages of this networking standard and the challenges our team has met working on BLE mesh projects.
If you’re choosing an out-of-the-box and easy-to-implement solution to build decentralized wireless networks, Bluetooth mesh may be an option.
This protocol can provide secure and reliable communication between multiple devices on a large-scale network. BLE mesh can compete with Wi-Fi, Z-wave, Zigbee, Thread, and other technologies in the context of the Internet of Things and smart connectivity.
However, this is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and like any other technology, it has both strong and weak points. Using our personal experience with Bluetooth mesh networks, we’ll shed some light on this standard to help you understand whether it works for you.
What Is A Bluetooth Mesh Network?
What is a mesh network, broadly speaking? A mesh network is a network of devices, or nodes, connected directly, dynamically, and non-hierarchically to as many other nodes as possible. The nodes cooperate with each other by exchanging data.
A Bluetooth low energy mesh network is a meshnet based on BLE technology.
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (Bluetooth SIG) first introduced Bluetooth Low Energy or BLE in 2009. In early 2010, it was completely integrated into Bluetooth 4.0. The new technology was designed for smart connectivity systems with low power requirements.
However, the abilities of BLE networks were quite limited. Bluetooth Low Energy allowed for one-to-one communication, and simple devices (like beacons) within a network could communicate only via the central hub.
The release of the Bluetooth mesh networking standard became a game-changer in 2017. The Mesh Profile specification, added to Bluetooth 5, provides the possibility for many-to-many communication.
Bluetooth mesh is intended for networks with a large number of nodes - mesh devices that broadcast messages. It targets the growing IoT market which continuously demands:
- more energy-efficient solutions;
- more security;
- more communicating devices;
- more flexible technologies.
As part of our IoT solution development services, we can build a BLE mesh network of diverse complexity for your project.
How BLE Mesh Network Works
What differentiates the Bluetooth LE mesh network from Zigbee/other forms of technology, in the first place, is broadcasting messages. Unlike the other wireless networks based on routing, the BLE mesh protocol applies the managed flood principle.
This approach offers a peer-to-peer communication model in which all nodes, or devices, communicate directly with each other. Managed flooding makes messaging efficient without complex routing algorithms. You don’t need to use the central hub but you can relay messages straight to the right nodes without any interruptions.
The self-sufficiency of the nodes, coupled with multipath messaging, facilitates the scalability of BLE mesh networking. It can help you create countless networks with innumerable nodes.
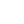
In a BLE mesh network, nodes use the publish/subscribe model for communication. Publishers send messages to multiple devices. To receive particular messages, a device must subscribe to various addresses (or a set of addresses).
This type of messaging gives you an opportunity to configure BLE mesh devices to form network segments of different scale and purpose. As a consequence of this configuring, technology becomes even more flexible and manageable.
BLE mesh architecture has a multi-layer structure typical of any communication network:
- The upper layers take responsibility for the contents of messages.
- The middle layers are responsible for the logic and behavior of the network.
- The lower layers define message transmission.
Bluetooth mesh networking places a strong focus on security. There are encryption and authentication systems for all messages based on the AES-CMAC and AES-CCM algorithms. The security keys protect the contents of messages and ensure sensitive communication between the nodes.
The use of security credentials protects the BLE mesh network from unauthorized access. Provisioning, or adding a device to the meshnet, is also secure. A new node provisioned on the network gets a unique ID and access to the security keys.
You can create a mesh network using literally any low energy Bluetooth chip or microcontroller that supports the technology. The popular manufacturers, such as Nordic Semiconductors, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, Silicon Labs, Qualcomm, and others, produce the hardware and provide SDK to build custom BLE mesh networks.
The main challenge is not just choosing hardware, but creating a viable meshnet. Within our electronic design and firmware development services, our engineers will select the right chip and build a mesh architecture according to your project requirements.
Why Use A Mesh Network?
Just like other Bluetooth LE networks, BLE mesh features low power consumption. Therefore, this technology works well when one needs to cover a large area and save energy at the same time.
The connection-based Bluetooth network requires a connection between two devices or a stable configured route so that a message could travel through several nodes until it reaches the addressee. But in a BLE mesh network, nodes can be disconnected without serious consequences. If one of the devices disappears, the initial node will continue broadcasting the data. The addressee will receive the packet with just a few seconds’ delay.
Most of the standard implementations provide no guarantee of this. However, the mesh network is different. It reconfigures itself. It is flexible, which is sometimes more important than a guaranteed speed and shorter delays.
Nodes in a Bluetooth mesh network may change their position without breaking the whole network structure and without losing transferred data. Data loss is possible only if the nodes leave the coverage area of the receiver.
BLE mesh nodes can communicate with Bluetooth 4.x and 5.x devices. A Bluetooth 4.x compatible device will be able to receive messages. But it will not become a fully-fledged node of the network as it can communicate only with the paired device.
Now, there are a growing number of devices that support BLE mesh. One of the most promising areas for Bluetooth mesh networking is mobile communication because smartphones are compatible with Bluetooth 4.0 and BLE.
BLE mesh technology is closely connected with beacons. BLE beacons are broadly used in sensor networks, indoor and outdoor positioning, and other low-power connected systems.
As a highly flexible, energy-efficient, and secure solution, BLE mesh can find use in traditional networking applications, such as:
- Home automation
- Industrial automation
- Smart lighting
- Asset tracking
- Proximity detection
Our development experience proves that you can use this technology as a nonstandard solution for your project. Further in our guide, we’ll give an example of a BLE mesh network used for an unconventional application.
BLE 5.x Mesh Compared to Similar Technologies
Apart from BLE mesh, there are other similar mesh networking technologies. The most popular of them include Zigbee and Thread. These protocols have much in common with Bluetooth mesh networking.
Announced in 2014, Thread is the youngest technology compared to Zigbee and BLE mesh. It is an Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) based mesh networking protocol designed for IoT systems.
This protocol has a limited number of routers (32 per network) and it is not appropriate for large-scale networks. However, you can connect up to 511 devices per router. So, this networking standard works well for high-density meshnets.
Thread is an IP-addressable out-of-the-box solution that you can easily integrate into your IPv6-based app. This standard has a sufficiently high data rate compared to similar technologies. Thread is fine for local IoT systems and it is not intended for long-distance data transmission.
Zigbee is much older than its competitors. It first appeared in 1998 and was standardized in 2003. Zigbee is a low-power and low-bandwidth wireless network. Its application areas include home automation, medical devices, industrial and building automation, and others.
This technology is intended for low data rate networks. It has a fixed maximum rate of 250 Kbits/sec.
Version 2.0 of Zigbee Smart Energy supports IPv6 and provides services for electric vehicles. Zigbee RF4CE is a standard developed for radio frequency remote controls. It finds use in diverse consumer electronics and low-cost remote control devices.
Zigbee supports different frequency and output power ranges and consequently different transmission distances. It can work with a variety of transceivers, including Bluetooth Low Energy. Zigbee is rarely supported by consumer electronics. So if you want to add a new device without a special Zigbee transceiver, like a smartphone, on your network, you’ll need to use a gateway.
Each of the three standards provides wireless mesh communication and is widely used in IoT and smart home systems. The technologies are suitable for networks with low bandwidth and low power consumption. Security is a significant feature of all the protocols.
Depending on the project requirements, Zigbee, Thread, and Bluetooth mesh standards can show roughly the same performance.
The main distinction of BLE mesh networking is that it uses Bluetooth instead of the Internet Protocol and managed flood messaging instead of routing.
IP-compatibility gives an advantage in cases when you need to connect devices that use IP addresses. If you want to introduce IP-based devices into a BLE mesh network, you need to think through addressing mechanisms.
In managed flooding, all nodes of the network receive and pass messages on unless they are subscribed to them. Devices don’t store this data so they don’t need much RAM.
When you use Zigbee and Thread, you should make certain that devices in the network have enough RAM to store routing tables.
The use of managed flooding in multi-node networks may create much noise since messages are relayed to all the nodes at once. That’s why this approach works better for low-density meshnets.
The routing mechanism applied in Zigbee and Thread assists you in directing messages to the destination nodes. This helps mitigate noise and use these protocols in high-density networks.
The flood-based approach engages every node of a BLE mesh network in communication which creates certain overhead. To reduce it, you can develop filtering algorithms or use virtual addresses with unique identifiers.
Compared to flood messaging, routing has a more complicated implementation. But at the same time, it provides faster data transfer with lower overhead.
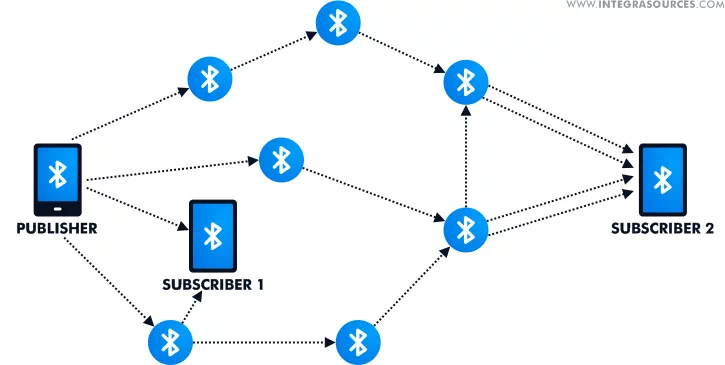
For one of the projects, we have compared the main characteristics of BLE 5.x Mesh, Zigbee, Thread, and our own Integra BLE networks. BLE mesh network had the lowest bandwidth, less than 1.5 kbit/sec for 100 bytes packet on six hops, and the largest delay (640 ms for the same packet and four hops).
BLE mesh has no guaranteed data delivery, unlike Zigbee or Thread. So, for a small amount of data that does not require fast and guaranteed delivery, it might be a good option.
Nowadays, all smartphones and most consumer electronics support Bluetooth. So you can easily integrate a Bluetooth network into the existing environment, making the implementation faster and less costly.
The strongest point of Bluetooth mesh networks is their survivability - you don’t have to worry much about the nodes’ relocation. The weakest points include heavy broadcast traffic and low throughput. The most suitable application of BLE mesh is a smart home and similar IoT projects that involve the transmission of small amounts of data.

Our Experience with Bluetooth Mesh Projects
Working with any new technology is always challenging for a developer. When the technology is young, it may lack the necessary documentation and use cases available online. In this situation, you resolve every issue by trial and error.
One of the non-standard commercial projects based on Bluetooth mesh and realized by Integra Sources is a network of Bluetooth devices for restaurants and bars. The standard BLE Mesh network realization fits the project well.

The devices in this network are stylish cubes located on the tables with NFC tags but not tied to them. The staff can relocate the cubes in any order, as the network is absolutely flexible.
Visitors to the restaurant can use these devices to call a waiter and ask for the check. The cubes also inform the waiting staff how long the guest has been kept waiting. Besides, the devices work as a table lamp.
The staff receive the data from the cubes using iOS smartphones and tablets that connect to the closest Bluetooth device. The latter becomes a gateway. This connection, however, does not affect the whole network configuration.
Data accumulated from the devices generate comprehensive statistics. Owners can use the data to optimize employee performance and improve the quality of service in the restaurants.
The arbitrary placement of the nodes makes it possible to create a completely different Bluetooth mesh network configuration. On the schemes below, you can see just some of the situations.
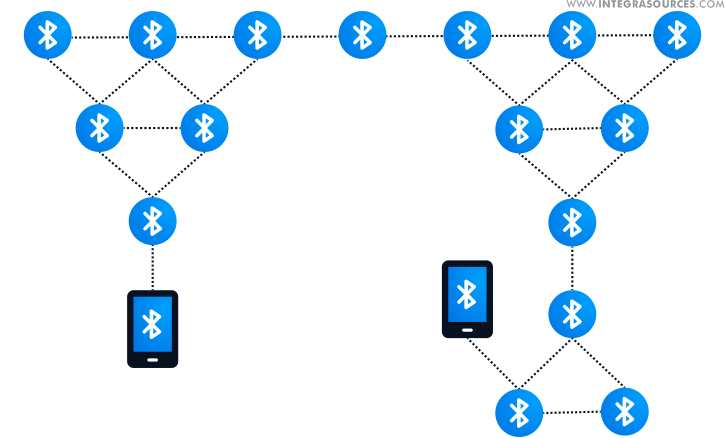
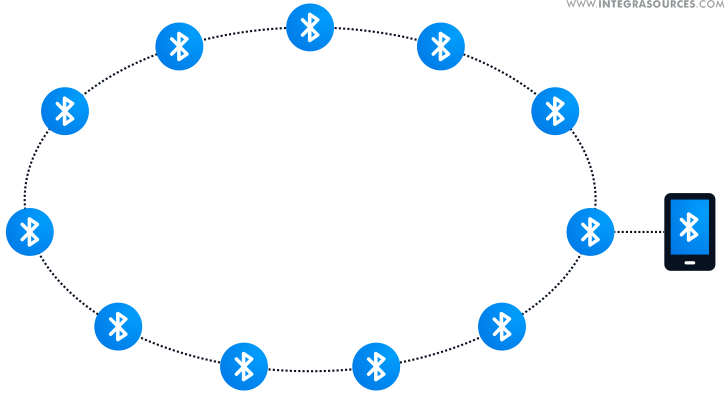
We performed several experiments on about 100 Bluetooth nodes to find the algorithms that can configure this network automatically.
The restaurant staff relocates the cubes and turns them on and off all the time. As a result, the physical topology of the network is constantly affected by the human factor. Besides, many restaurants have several rooms.
It took our team hundreds of hours to develop methods and rules for building and rebuilding the graph in real time. But the result was worth it. We managed to make the system both reliable and flexible.
A standard BLE mesh network does not involve routing. Each node receives packets from all other nodes and retransmits them further. As the number of nodes increases, so does the number of data transmission operations. As a result, the performance of the network drops.
Even with a low message time-to-live (TTL), it is easy to imagine the broadcast storm that a 1000-node mesh network could generate. The delays and latency only grow with the number of nodes and the number of packets sent between them.
A BLE mesh network can support over 30 thousand nodes. But in practice, even a hundred devices can overload the network and disrupt the work of the whole ecosystem.
For the restaurant cubes project, we had to find a way to reduce the effect of this storm. First of all, we added a certain TTL to each packet of the node. This has decreased the traffic in the network.
To reduce the consequences of the storm, we decided to replace the managed flood messaging native to BLE mesh networks by routing mechanisms.
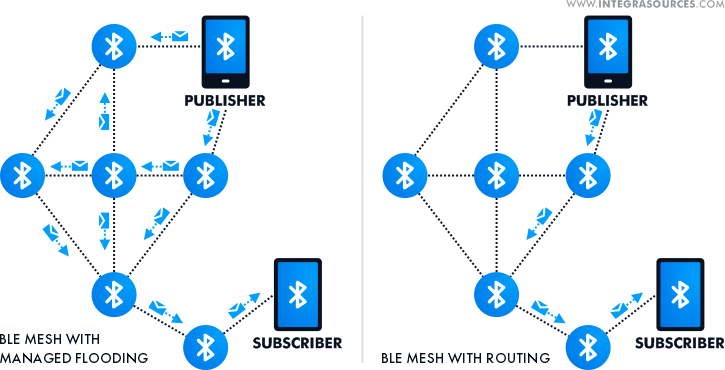
Our engineers developed routing tables for each node. The routing algorithms provided fast and guaranteed data delivery from the devices to the gateway.
We introduced measurements of signal strength or RSSI to build strong connections between the modes and make the communication efficient.
In theory, the maximum physical speed of a mesh network with Bluetooth 5.x devices (including the service data on the beacon, packet type, etc.) is 2 Mbit per second. However, such speed is impossible to reach in real data transmission. So the potential of using Bluetooth mesh networks is still not that great.
To estimate the real bandwidth of data transfer within a mesh network, you should take into account two basic criteria:
- the number of devices;
- the distance between the devices and the BLE network topology.
In one of our asset tracking projects, as well as in the restaurant mesh network, the data throughput rate was about 80 kbit/s. However, this data rate allows for timely notifications and even imaging with low power consumption.
One of our customers wanted to implement a mesh network for an industrial company to track employees and transport movement within a facility.
However, they needed a high bandwidth and the highest reliability at the same time, while transferring data for quite a long distance, about one kilometer. All the devices, aside from one gateway, were battery-powered.
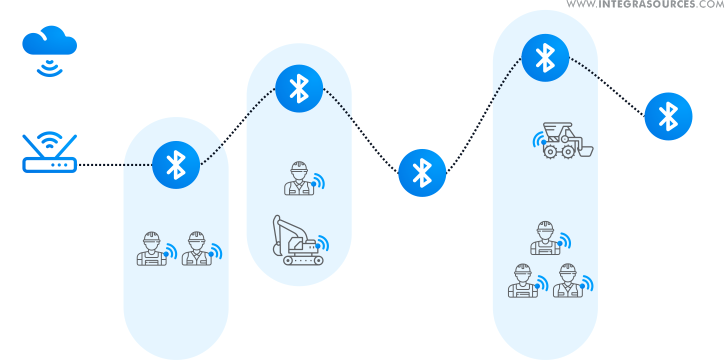
Thus, a BLE mesh network wouldn’t be able to provide reliable data delivery or high throughput. Instead, our team created a custom meshnet based on the BLE protocol that wouldn’t cause a broadcast storm.
We have built a network that reconfigures itself automatically. The network topology gets updated upon provisioning a new device. The number of provisioned devices is unlimited. Each device acts as both a node and a router.

A direct connection between the neighboring nodes and routing the data to the gateway proved to be more effective for this project. The developed people and asset tracking solution guaranteed message delivery within the hard-to-reach industrial area. Using multiple beacons, the solution assists in tracking employees and equipment located even at a long distance from the gateway.
Conclusion: Yes or No for BLE Mesh?
The BLE mesh networking technology has undeniable advantages. However, it cannot be considered universal since its applications are limited. If it meets certain business needs, it should be set up properly, which can require a lot of experimentation and tests.
However, our experience proves that this is a robust technology, especially for the Internet of Things solutions. BLE mesh meets the latest requirements of smart connectivity - it is low-power, large-scale, flexible, and secure.
Working on Bluetooth mesh projects, we complete all necessary types of tasks:
- provide a custom gateway;
- create a mesh network topology;
- write firmware for the nodes and the gateway;
- optimize the topology by making it compatible with the existing devices and system.
So if you need a low power wireless system with scalable connectivity and secure data transfer, we can create a BLE mesh network for your particular project.
We hope that our BLE mesh guide gave you an idea of this networking technology. If you still have doubts about using BLE mesh technology for your product, feel free to contact us and get our professional advice.
Share this article


Related
materials


BLE-based Indoor Positioning Solution for Online Advertising
This beacon system is installed in shops, restaurants, and similar locations. It promotes businesses by sending push notifications to bypassers.
LEARN MORE
LEARN MORE

Bluetooth Indoor Positioning Systems: Implementation Features & Alternatives
Indoor positioning provides a lot of opportunities for businesses, enabling them to optimize work processes and improve service quality. Bluetooth...
LEARN MORE
LEARN MORE

Bluetooth Mesh: Technology Overview, Examples, Alternatives, and First-Hand Experience
Hands-on experience from our team, which dug into this quite new technology. We have already implemented several projects based on...
LEARN MORE
LEARN MORE