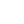
Real-Time Signal Processing for Wearable Electrocardiogram Device
Noise can be harmful. Exposure to noise increases stress levels which leads to raised heart rate and blood pressure. The University of East London had been conducting a study that examined how exposure to noise may adversely affect the cardiovascular systems of children and adults.
To carry out their research, the Research Center built a portable electrocardiogram (ECG) device for the participants in the experiment. This device was designed to record heart rate and individual noise levels. With these records, researchers could analyze how different noise levels affect heart rates and heart rate variability (HRV).
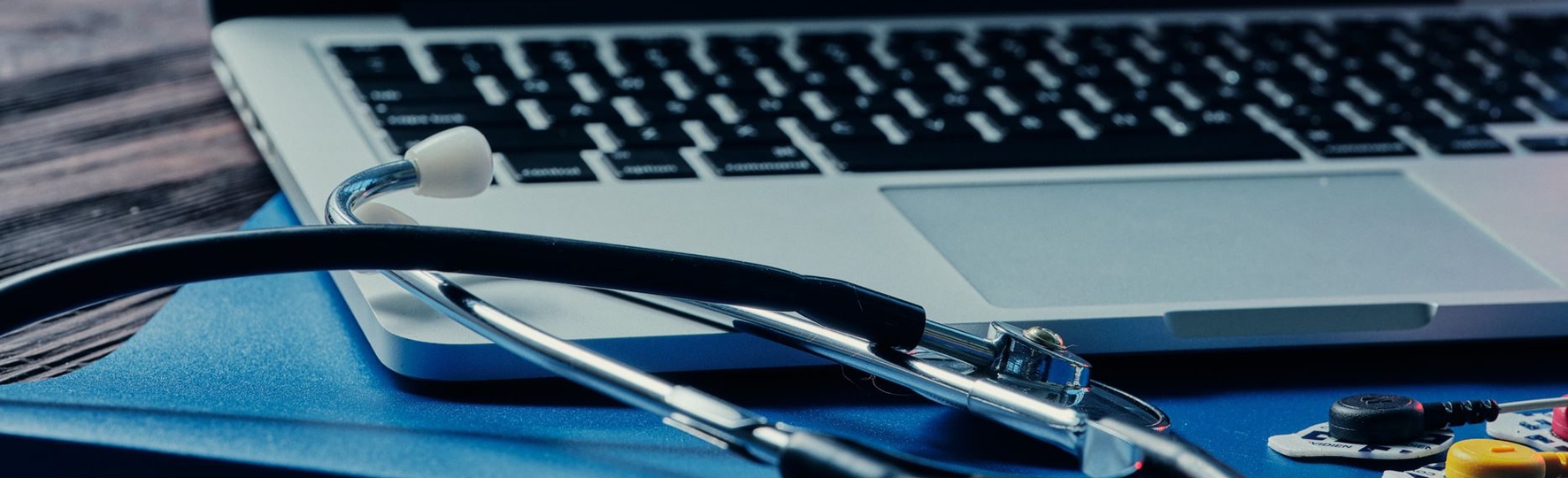

Request
The research team was looking for an experienced development company that could build firmware for their ECG wearable device. They also needed to create an application that could provide data visualization capabilities for further heart rate research.
Solution
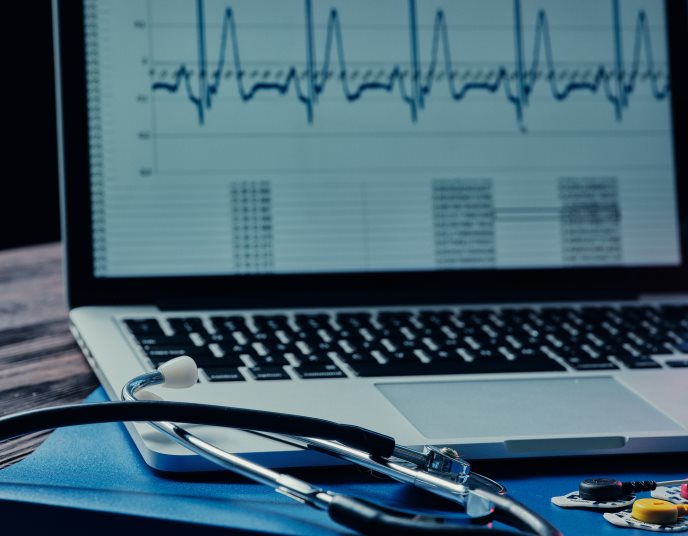
Integra Sources provided firmware development so the ECG device could perform its function: record the data from all its sensors and send this data to mobile phones via Bluetooth where it is displayed in real-time. We also provided Android mobile application development for our client.

Make some noise
Make some noise
Technologies Used
- We used nRF51 with BLE 4.0 support and Cortex-M0 core as MCU in this project.
- FreeRTOS was used for firmware development.
- The firmware was implemented using C/C++.
- Microsoft Visual Studio with Visual GDB plugin was used for firmware implementation.
- The android application was implemented in the Android Studio using Java language.
- The device has a microphone, ECG, accelerometer, and a thermometer sensor
How it works
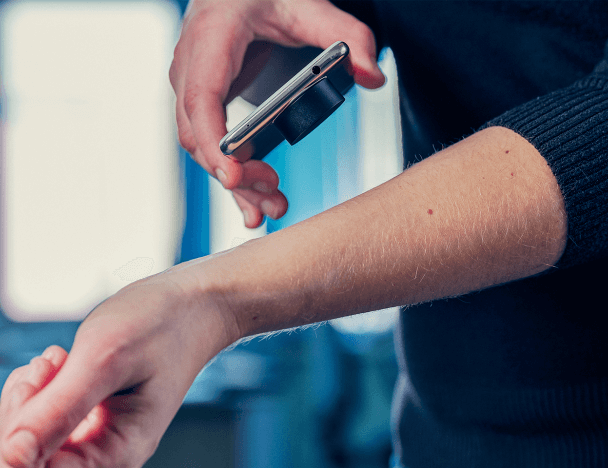
Participants in the experiment (children and adults) are equipped with a wearable ECG device placed on their skin. As they go about their day, electrical impulses released by the heart are picked up, processed by the microprocessor and recorded. At the end of the day, the participants come back to the lab where the researchers take off their ECG devices and study the heart's electrical activity in response to environmental noise, including from road traffic and aircraft.

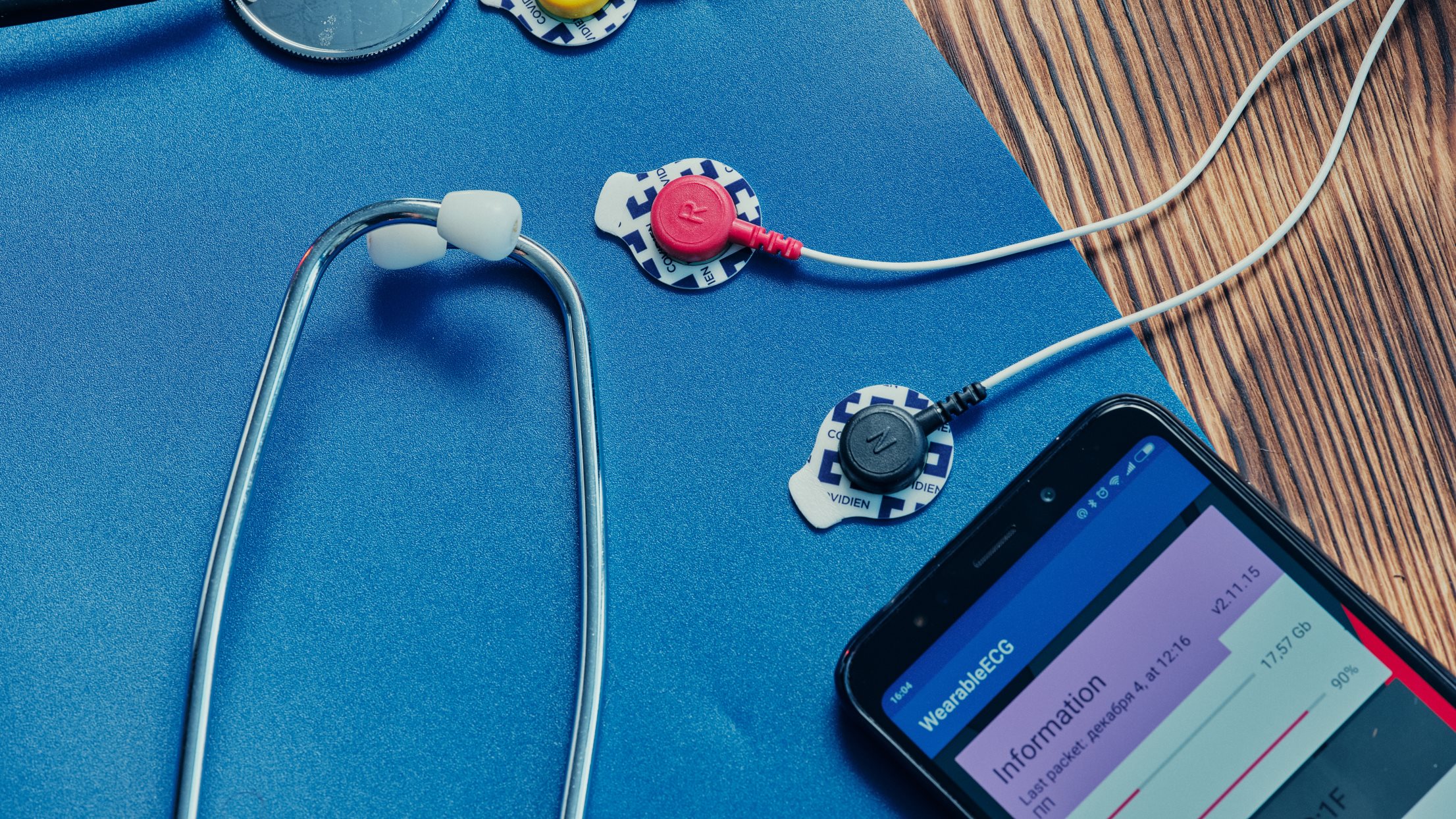
Challenges solved: Real-time data processing
The main job of the firmware is to enable data transfer from the wearable ECG device to Android smartphones via Bluetooth 4.0+ in real time. As soon as the data arrives at the smartphone, the GPS coordinates of the phone are added to the data package. The device collects the data from the following sensors:
- ECG: 250Hz
- Accelerometer: 30Hz
- Thermometer: 1Hz
- Microphone: 11,2kHz
We needed to implement a continuous data transfer. To make it possible for the ECG device to keep the data when the connection with a smartphone is lost, we implemented temporary data storage in the flash memory.
Another major tech challenge was related to the data transfer speed that Bluetooth channels could handle. The required speed was 2MB/sec. But after we made our calculations, the realistic speed appeared to be lower – 2-3KB/sec in that particular case. To optimize the data transfer rate our team implemented compression achieved by encoder and decoder.
Result
With the wearable ECG device and a user-friendly mobile app, it became possible for scientists to perform their research and investigate the effects of noise exposure on children and adults’ blood pressure and heart health.

Real-time data transfer speed
Data loss
Continuous data transfer
Integra's team helped us clarify our requirements and change systems architecture to achieve the final goal. I'd say that the flexibility and enthusiasm of both engineering and management teams throughout the whole project were some of the things we value most in our collaboration.
Scope of work
- Firmware development
- Android app development
You might also like...
Medical Alert Bracelet That Delivers Assistance at the Touch of a Button
A bracelet designed for patients at military hospitals and clinics in the USA. It notifies hospital staff about an emergency with the patient. 
LEARN MORE 

SkinView iOS App for Identifying Skin Cancer with Computer Vision
The app utilizes computer vision algorithms to analyze moles for melanoma detection, achieving 80% diagnostic accuracy and rapid processing times under 0.1 seconds. 
LEARN MORE